논문 정리 URL 변경
27 Jan 2020 |앞으로 논문은 여기에 정리한다.
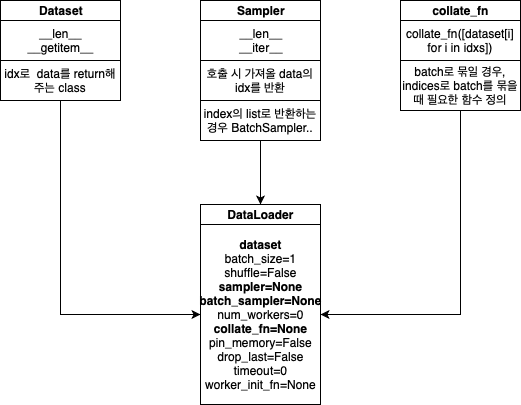
__len__, __getitem__을 구현해야함import torch
import numpy as np
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, ConcatDataset, Sampler, RandomSampler, BatchSampler
먼저 fixed length dataset을 다루기 위해 Dataset과 DataLoader만 다뤄보자
__len__과 __getitem__을 구현다음은 Fixed length를 가지는 간단한 데이터셋 예제이다.
[0, 0, 0], [1, 2, 3], [2, 4, 6], ...[0, 1, 2, 3, ...]class MapDataset(Dataset):
def __len__(self):
return 10
def __getitem__(self, idx):
return {"input":torch.tensor([idx, 2*idx, 3*idx],
dtype=torch.float32),
"label": torch.tensor(idx,
dtype=torch.float32)}
map_dataset = MapDataset()
dataset으로 유의미한 data를 뽑아오기 위한 것이 DataLoader이다.
순서를 그대로 지키는 것을 알 수 있다.
기본 옵션은 다음과 같다.
DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=1, shuffle=False, sampler=None,
batch_sampler=None, num_workers=0, collate_fn=None,
pin_memory=False, drop_last=False, timeout=0,
worker_init_fn=None)
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(map_dataset)
for data in dataloader:
print(data['label'])
tensor([0.])
tensor([1.])
tensor([2.])
tensor([3.])
tensor([4.])
tensor([5.])
tensor([6.])
tensor([7.])
tensor([8.])
tensor([9.])
batch_size를 주면 batch로 뽑을 수 있다. 물론 이번에도 순서대로 batching을 한다.
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(map_dataset,
batch_size=4)
for data in dataloader:
print(data['input'].shape, data['label'])
torch.Size([4, 3]) tensor([0., 1., 2., 3.])
torch.Size([4, 3]) tensor([4., 5., 6., 7.])
torch.Size([2, 3]) tensor([8., 9.])
dataset은 index로 data를 가져오도록 설계되었기 때문에, shuffle을 하기 위해서 index를 적절히 섞어주면 된다.
그 것을 구현한 것이 Sampler이다.
__len__과 __iter__를 구현하면 된다.RandomSampler로 각 data를 random하게 가져오며, batch_size를 4로 해보았다.
point_sampler = RandomSampler(map_dataset)
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(map_dataset,
batch_size=4,
sampler=point_sampler)
for data in dataloader:
print(data['input'].shape, data['label'])
torch.Size([4, 3]) tensor([5., 7., 4., 8.])
torch.Size([4, 3]) tensor([9., 0., 2., 6.])
torch.Size([2, 3]) tensor([1., 3.])
batch 단위로 sampling할 때 쓴다. bucketing할 때 외에는 언제 쓸까…
index의 list를 반환하면 batch_sampler로 쓸 수 있음def __init__(self, sampler, batch_size, drop_last) 요래 생김point_sampler = RandomSampler(map_dataset)
batch_sampler = BatchSampler(point_sampler, 3, False)
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(map_dataset,
batch_sampler=batch_sampler)
for data in dataloader:
print(data['input'].shape, data['label'])
torch.Size([3, 3]) tensor([1., 2., 4.])
torch.Size([3, 3]) tensor([3., 5., 0.])
torch.Size([3, 3]) tensor([7., 6., 8.])
torch.Size([1, 3]) tensor([9.])
collate_fn([dataset[i] for i in indices])collate_fn을 만들어서 넘겨줘야함이제 input의 size가 data마다 다른 dataset을 만들어보자.
class VarMapDataset(Dataset):
def __len__(self):
return 10
def __getitem__(self, idx):
return {"input":torch.tensor([idx] * (idx+1),
dtype=torch.float32),
"label": torch.tensor(idx,
dtype=torch.float32)}
var_map_dataset = VarMapDataset()
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(var_map_dataset)
for data in dataloader:
print(data['input'])
tensor([[0.]])
tensor([[1., 1.]])
tensor([[2., 2., 2.]])
tensor([[3., 3., 3., 3.]])
tensor([[4., 4., 4., 4., 4.]])
tensor([[5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5.]])
tensor([[6., 6., 6., 6., 6., 6., 6.]])
tensor([[7., 7., 7., 7., 7., 7., 7., 7.]])
tensor([[8., 8., 8., 8., 8., 8., 8., 8., 8.]])
tensor([[9., 9., 9., 9., 9., 9., 9., 9., 9., 9.]])
위의 dataset을 이용하여 batch_size를 2 이상으로 DataLoader를 부르면 error가 난다.
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(var_map_dataset,
batch_size=2)
for data in dataloader:
print(data['input'].shape, data['label'])
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
RuntimeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-17-d98b49d5b0d4> in <module>
1 dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(var_map_dataset,
2 batch_size=2)
----> 3 for data in dataloader:
4 print(data['input'].shape, data['label'])
...
RuntimeError: invalid argument 0: Sizes of tensors must match except in dimension 0. Got 1 and 2 in dimension 1 at /Users/soumith/b101_2/2019_02_08/wheel_build_dirs/wheel_3.7/pytorch/aten/src/TH/generic/THTensorMoreMath.cpp:1307
따라서 batch로 묶일 모든 데이터를 잘 묶어주는(collate) 함수가 필요한 것! 역시나 예제로 살펴보자
def make_batch(samples):
inputs = [sample['input'] for sample in samples]
labels = [sample['label'] for sample in samples]
padded_inputs = torch.nn.utils.rnn.pad_sequence(inputs, batch_first=True)
return {'input': padded_inputs.contiguous(),
'label': torch.stack(labels).contiguous()}
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(var_map_dataset,
batch_size=3,
collate_fn=make_batch)
for data in dataloader:
print(data['input'], data['label'])
tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[1., 1., 0.],
[2., 2., 2.]]) tensor([0., 1., 2.])
tensor([[3., 3., 3., 3., 0., 0.],
[4., 4., 4., 4., 4., 0.],
[5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5.]]) tensor([3., 4., 5.])
tensor([[6., 6., 6., 6., 6., 6., 6., 0., 0.],
[7., 7., 7., 7., 7., 7., 7., 7., 0.],
[8., 8., 8., 8., 8., 8., 8., 8., 8.]]) tensor([6., 7., 8.])
tensor([[9., 9., 9., 9., 9., 9., 9., 9., 9., 9.]]) tensor([9.])
sampler = RandomSampler(var_map_dataset)
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(var_map_dataset,
batch_size=3,
sampler=sampler,
collate_fn=make_batch)
for data in dataloader:
print(data['input'], data['label'])
tensor([[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[3., 3., 3., 3., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[9., 9., 9., 9., 9., 9., 9., 9., 9., 9.]]) tensor([0., 3., 9.])
tensor([[5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 0., 0.],
[7., 7., 7., 7., 7., 7., 7., 7.],
[2., 2., 2., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]]) tensor([5., 7., 2.])
tensor([[8., 8., 8., 8., 8., 8., 8., 8., 8.],
[4., 4., 4., 4., 4., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]]) tensor([8., 4., 1.])
tensor([[6., 6., 6., 6., 6., 6., 6.]]) tensor([6.])
def _bucket_boundaries(max_length, min_length=8, length_bucket_step=1.1):
assert length_bucket_step > 1.0
x = min_length
boundaries = []
while x < max_length:
boundaries.append(x)
x = max(x + 1, int(x * length_bucket_step))
return boundaries
def batching_scheme(batch_size,
max_length,
min_length_bucket,
length_bucket_step,
drop_long_sequences=False,
shard_multiplier=1,
length_multiplier=1,
min_length=0):
max_length = max_length or batch_size
if max_length < min_length:
raise ValueError("max_length must be greater or equal to min_length")
boundaries = _bucket_boundaries(max_length, min_length_bucket,
length_bucket_step)
boundaries = [boundary * length_multiplier for boundary in boundaries]
max_length *= length_multiplier
batch_sizes = [
max(1, batch_size // length) for length in boundaries + [max_length]
]
max_batch_size = max(batch_sizes)
highly_composite_numbers = [
1, 2, 4, 6, 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 120, 180, 240, 360, 720, 840, 1260, 1680,
2520, 5040, 7560, 10080, 15120, 20160, 25200, 27720, 45360, 50400, 55440,
83160, 110880, 166320, 221760, 277200, 332640, 498960, 554400, 665280,
720720, 1081080, 1441440, 2162160, 2882880, 3603600, 4324320, 6486480,
7207200, 8648640, 10810800, 14414400, 17297280, 21621600, 32432400,
36756720, 43243200, 61261200, 73513440, 110270160
]
window_size = max(
[i for i in highly_composite_numbers if i <= 3 * max_batch_size])
divisors = [i for i in range(1, window_size + 1) if window_size % i == 0]
batch_sizes = [max([d for d in divisors if d <= bs]) for bs in batch_sizes]
window_size *= shard_multiplier
batch_sizes = [bs * shard_multiplier for bs in batch_sizes]
max_batches_per_window = window_size // min(batch_sizes)
shuffle_queue_size = max_batches_per_window * 3
ret = { "boundaries": boundaries,
"batch_sizes": batch_sizes,
"min_length": min_length,
"max_length": (max_length if drop_long_sequences else 10**9),
"shuffle_queue_size": shuffle_queue_size}
return ret
class VarDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, num_data):
self.num_data = num_data
self.lengths = [i for i in range(1, num_data+1)] # 각 source들의 length를 알아야함
def __len__(self):
return self.num_data
def __getitem__(self, idx):
return {"input":torch.tensor([idx] * (idx+1),
dtype=torch.float32),
"label": torch.tensor(idx,
dtype=torch.float32)}
class BucketSampler(Sampler):
def __init__(self, sampler, batch_size, drop_last=False):
scheme = batching_scheme(
batch_size=batch_size,
max_length=1000,
min_length_bucket=1,
length_bucket_step=1.1)
self.boundaries = scheme['boundaries']
self.batch_sizes = scheme['batch_sizes']
self.sampler = sampler
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.drop_last = drop_last
def __iter__(self):
buckets = [[] for i in range(len(self.boundaries))]
for idx in self.sampler:
# sampler에서 dataset을 가져와서 data의 length를 잼
length = self.sampler.data_source[idx]["input"].size(0)
for i, boundary in enumerate(self.boundaries):
if length <= boundary:
buckets[i].append(idx)
if len(buckets[i]) == self.batch_sizes[i]:
yield buckets[i]
buckets[i] = []
break
if not self.drop_last:
for bucket in filter(len, buckets):
yield bucket
def __len__(self):
raise NotImplementedError("BucketSampler cannot know the total number of batches.")
def make_batch(samples):
inputs = [sample['input'] for sample in samples]
labels = [sample['label'] for sample in samples]
padded_inputs = torch.nn.utils.rnn.pad_sequence(inputs, batch_first=True)
return {'input': padded_inputs.contiguous(),
'label': torch.stack(labels).contiguous()}
var_dataset = VarDataset(1000)
sampler = RandomSampler(var_dataset)
bucketing = BucketSampler(sampler, 2000)
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(var_dataset,
batch_sampler=bucketing,
collate_fn=make_batch)
for i, data in enumerate(dataloader):
print(data['input'].shape, data['label'])
if i > 3:
break
torch.Size([3, 542]) tensor([500., 541., 521.])
torch.Size([2, 780]) tensor([779., 778.])
torch.Size([2, 968]) tensor([967., 901.])
torch.Size([2, 942]) tensor([909., 941.])
torch.Size([2, 803]) tensor([802., 765.])
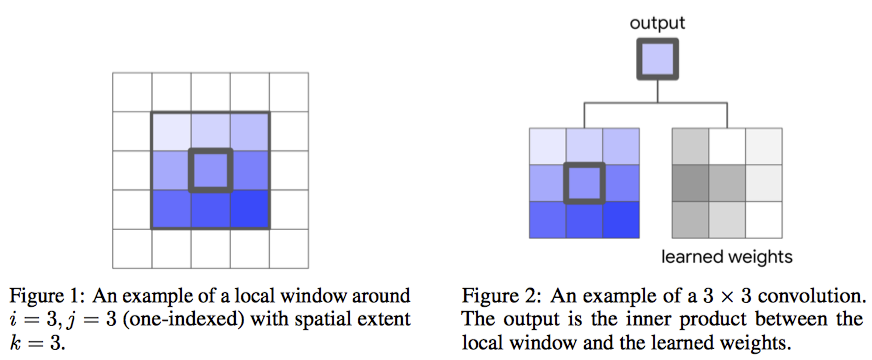
그림으로 보면 간단!
이것도 그림으로 보면 간결하다.
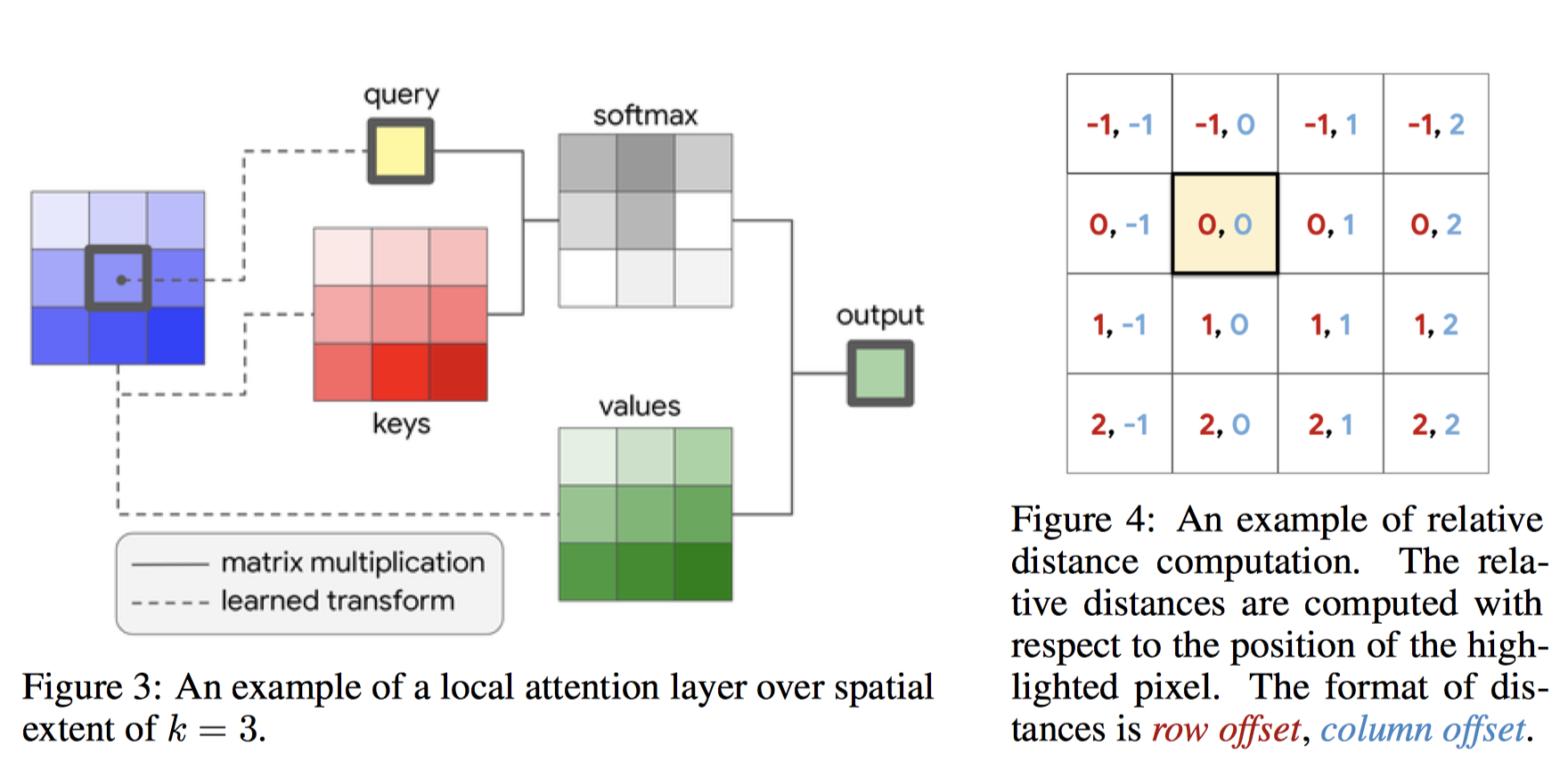
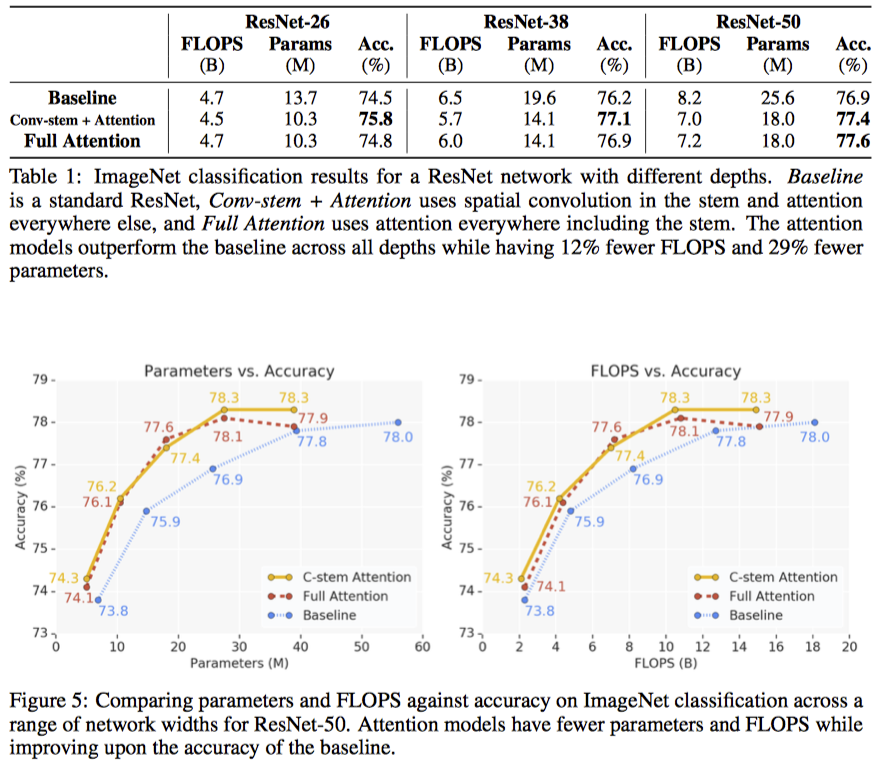
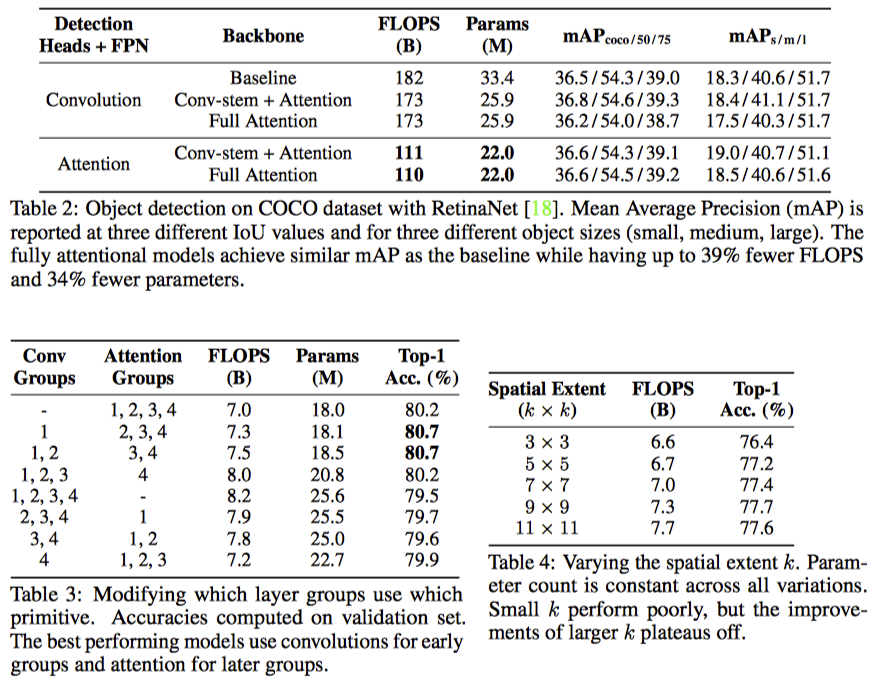
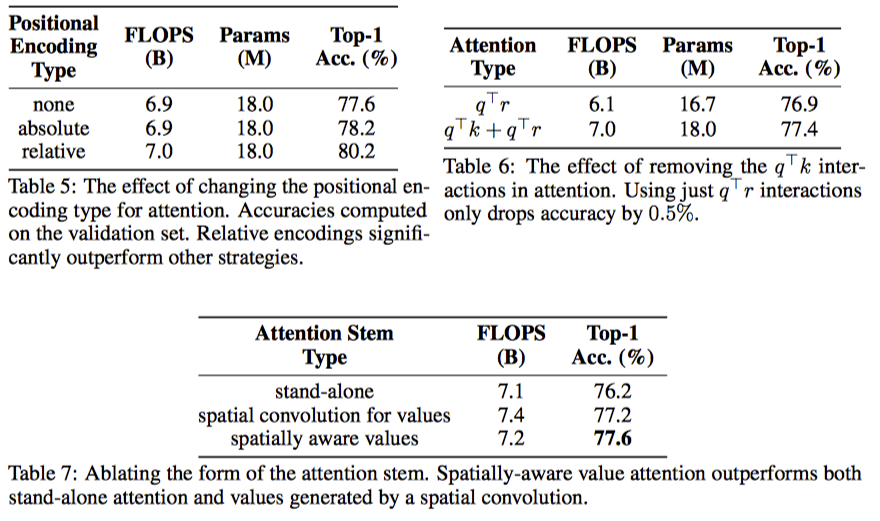
이렇게 하면, In/Out channel이 128일 때, k=3인 convolutional layer와 같은 파라미터 갯수로 k=19인 layer를 만들 수 있다고 한다.
위에서 정의한 local attention layer를 primitive로 삼아서, 어떻게 fully attentional architecture를 만들 수 있을까?
stride 2인 7 x 7 convolution + stride 2인 3 x 3 maxpooling으로 이루어짐