GPyOpt - 처음 tutorial 진행
17 Oct 2017 | bayesian inferencefrom GPyOpt.methods import BayesianOptimization
import numpy as np
# --- Define your problem
def f(x):
return (6*x - 2)**2 * np.sin(12 * x - 4)
bounds = [(0,1)]
# --- Solve your problem
myBopt = BayesianOptimization(f=f, bounds=bounds)
myBopt.run_optimization(max_iter=16)
myBopt.plot_acquisition()
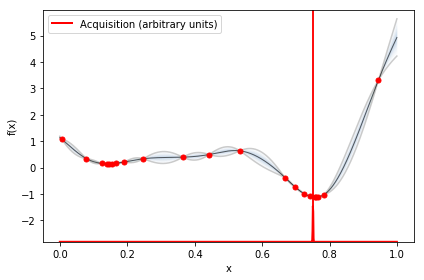
print(myBopt.x_opt)
print(myBopt.Y_new)
[ 0.75506832]
[[-5.66412991]]
domain 여러개 확인..
tensorflow에 적용하기 전에, discrete한게 되는지 봐야함.
from GPyOpt.methods import BayesianOptimization
import numpy as np
# --- Define your problem
def f(x):
return (6*x[0,0] - 2)**2 * np.sin(12 * x[0, 1] - 4)
domain = [{'name': 'a',
'type': 'continuous',
'domain':(0,10)},
{'name': 'test',
'type': 'discrete',
'domain':(0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10),
'dimensionality': 1}]
# --- Solve your problem
myBopt = BayesianOptimization(f=f, domain=domain)
myBopt.run_optimization(max_iter=5)
myBopt.plot_acquisition()
myBopt.X
array([[ 2.0503028 , 6. ],
[ 2.44130349, 4. ],
[ 5.74897004, 7. ],
[ 2.66912911, 9. ],
[ 6.31059492, 8. ],
[ 7.10601309, 7. ],
[ 8.53670111, 6. ],
[ 10. , 5. ],
[ 9.49270161, 7. ],
[ 10. , 8. ]])
myBopt.x_opt
array([ 9.49270161, 7. ])
myBopt.Y
array([[ -9.52947568e+01],
[ 2.83173048e+00],
[ -1.04939570e+03],
[ -6.31711134e+01],
[ -1.00254584e+03],
[ -1.64119927e+03],
[ -2.17534541e+03],
[ -1.75449757e+03],
[ -3.00172758e+03],
[ -2.62212386e+03]])
