unittest로 안전한 코드 관리를~
28 Oct 2016 | python debug unittestUnittest
Python에서는 unittest 모듈이 존재한다. 이를 사용하면 단위 테스트를 쉽게 할 수 있다.
unittest의 모듈에는 다음 녀석들이 있다.
- TestCase Class : 실제 test code를 넣을 녀석
- TestSuite Class : testcase들을 묶어서 돌릴 녀석
그림으로 표현하면 다음과 같다.
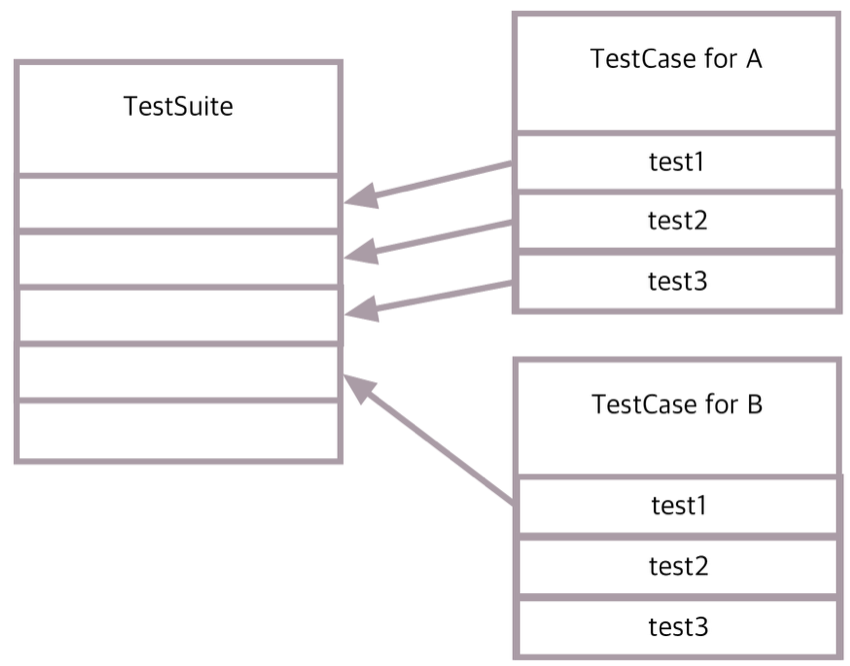
먼저 TestCase 작성법과 TestCase만으로 돌리는 방법을 살펴보자.
TestCase
unittest.TestCase를 상속받아서 새로운 testcase를 만든다.
setUp: 테스트 코드 시작시 공통적으로 넣을 코드를 넣는다.test~:setUp이후 테스트할 코드. 복수의 함수를 만든다.tearDown:test~가 끝난 후 공통으로 처리해야할 코드를 넣는다.
예제를 보자.
# coding: utf-8
import unittest
def sum(a,b):
return a+b
class ModuleTest1(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self):
pass
def tearDown(self):
pass
def testsum1(self):
self.assertEqual(sum(1,2),3)
def testsum2(self):
self.assertEqual(sum(1,-1),0)
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
####실행결과
..
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Ran 2 tests in 0.000s
OK
자주쓰는 함수
테스트 할 때 자주 쓰는 녀석들. 실제 사용해보니 Equal은 결과값이 다른 경우 쉘에 결과값을 보여주기 때문에 더 유용하다.
assertEqual(a, b, [msg])assertTrue(sentence, [msg])assertFalse(sentence, [msg])
Test Suite
이제 test suite를 사용해 묶어서 돌리는 방법을 보자. 코드로 보는 것이 빠르다.
testSuite = unittest.TestSuite()
for testmethod in ('testsum1', 'testsum2'):
testSuite.addTest(ModuleTest1(testmethod))
runner = unittest.TextTestRunner()
runner.run(testSuite)
테스트케이스를 저렇게 하나씩 넣는게 귀찮지.. class에서 함수를 긁어올 수는 없을까?해서 만들어보았다.
다음 코드는 class에서 test가 들어간 function들을 읽어오는 코드이다.
from types import FunctionType
class ModuleTest(unittest.TestCase):
def testA(self):
self.assertEqual(True,True)
for key, value in ModuleTest.__dict__.items():
if 'test' in key and isinstance(value, FunctionType):
print key
# testA
Code Coverage
위에서는 unittest를 하는 방법을 알아보았다. 해당 unittest를 통하여 코드를 얼마나 커버하는지 알 수 있다면 코드 품질 관리가 훨씬 좋을 것이다.
기본 모듈은 못찾았는데 pip install coverage로 coverage를 잴 수 있다.
coverage help를 쳐보면 기본 사용방법이 나온다.
usage: coverage <command> [options] [args]
Commands:
annotate Annotate source files with execution information.
combine Combine a number of data files.
erase Erase previously collected coverage data.
help Get help on using coverage.py.
html Create an HTML report.
report Report coverage stats on modules.
run Run a Python program and measure code execution.
xml Create an XML report of coverage results.
돌려보기
아까 만든 unittest를 test.py라 가정하자. 그러면 한줄만 치면 된다.
coverage run test.py
결과보기
결과는 terminal, html 두가지정도 있다. (xml도 있지만 안해봄..)
terminal 결과
coverage report로 볼 수 있다. 간단히 볼 때 좋다. 그러나 어떤 코드가 uncover인지 알고싶다면 html로 결과를 보는 것이 좋다.
Name Stmts Miss Cover
-----------------------------------------------------------------
hulkFlaskFunctions/__init__.py 0 0 100%
hulkFlaskFunctions/flaskPrettyPrinter.py 6 0 100%
hulkFlaskFunctions/hulkBaseValidate.py 13 3 77%
hulkFlaskFunctions/hulkConverterUnitTest.py 32 3 91%
hulkFlaskFunctions/hulkEquationConverter.py 45 6 87%
hulkFlaskFunctions/hulkPostCalculate.py 48 3 94%
...
hulkMathUtil/hulkSubstitute.py 21 0 100%
hulkUnittest.py 231 4 98%
-----------------------------------------------------------------
TOTAL 1540 148 90%
html 결과
coverage html을 수행하면 htmlcov란 폴더가 생긴다. 이 폴더 안의 index.html을 열면 html 결과를 볼 수 있다.
소스를 누르면 다음처럼 커버가 안된 부분이 빨간색으로 나온다.

coverage에서 코드 빼기
코드에서 절대 타지 않는 부분이 있을 수 있다. 예를들면 python3, python2 호환코드라면 python3로 돌리면 2용 코드들이 돌아가지 않는다. 또는 오픈소스를 사용했는데 오픈소스의 커버리지는 재기 싫을 수 있다. 이를 위해 두가지 방법이 존재한다.
- code의 일부분을 coverage에서 제외하기
- 특정 directory를 coverage에서 제외하기
code의 일부분을 coverage에서 제외하기
# pragma: no cover 주석을 달면 해당 branch는 커버리지에서 제외한다.
class MyPrettyPrinter(pprint.PrettyPrinter):
def format(self, _object, context, maxlevels, level):
if sys.version_info[0] == 2:
if isinstance(_object, unicode): # pragma: no cover
return "'%s'" % _object.encode('utf8'), True, False
elif isinstance(_object, str): # pragma: no cover
_object = unicode(_object, 'utf8')
return "'%s'" % _object.encode('utf8'), True, False
return pprint.PrettyPrinter.format(self,
_object,
context,
maxlevels,
level)
위의 코드를 돌린 결과를 html로 보면
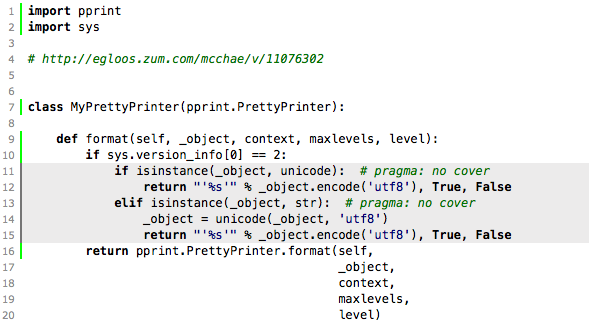
이렇게 회색 처리가 되면서 coverage에서 빠지게 된다.
특정 directory를 coverage에서 제외하기
정확한 config file을 알고싶진 않아서 방법만 제시한다.
다음처럼 [run] 부분에 omit = path를 넣는다.
그리고 file로 저장한다 (예제에서는 coverage_config)
[run]
omit = hulkFlaskFunctions/latex2sympy/*
[report]
# Regexes for lines to exclude from consideration
exclude_lines =
# Have to re-enable the standard pragma
pragma: no cover
# Don't complain about missing debug-only code:
def __repr__
if self\.debug
# Don't complain if tests don't hit defensive assertion code:
raise AssertionError
raise NotImplementedError
# Don't complain if non-runnable code isn't run:
if 0:
if __name__ == .__main__.:
ignore_errors = True
[html]
directory = coverage_html_report
coverage run --rcfile=coverage_config test.py로 돌리면 hulkFlaskFunctions/latex2sympy/*에 해당하는 모든 소스가 coverage에서 무시된다.
